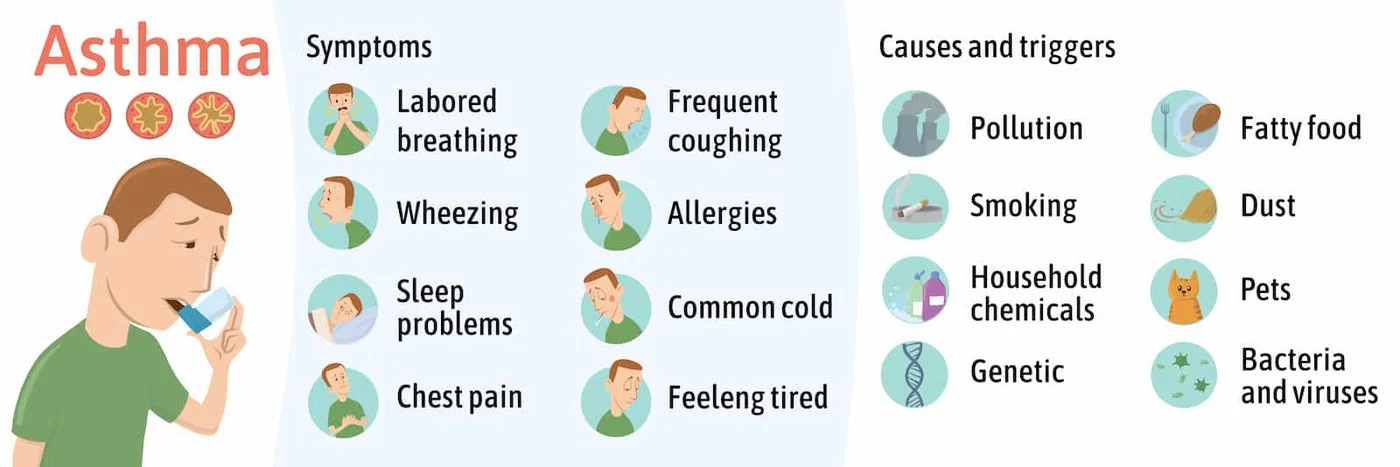
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions worldwide, characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to symptoms like wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. While asthma cannot be cured, effective management strategies can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. This blog explores three essential steps to achieving better asthma control, focusing on medication adherence, environmental management, and lifestyle adjustments. Buy Aerocort Inhaler and Asthalin inhaler is used to relieve symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, breathing difficulty, coughing, etc.
Step 1: Medication Adherence and Management
- Understanding Asthma Medications:
- Asthma medications are categorized into two main types:
- Relievers (Quick-Relief Medications): such as short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs) like albuterol, provide rapid relief during asthma attacks by relaxing the muscles around the airways.
- Controllers (Long-Term Control Medications): like inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs), leukotriene modifiers, and biologics, are used daily to reduce inflammation and prevent asthma symptoms.
- Asthma medications are categorized into two main types:
- Developing a Personalized Asthma Action Plan:
- Work with your healthcare provider to create an asthma action plan tailored to your needs. This plan outlines daily medications, instructions for managing worsening symptoms, and when to seek emergency care.
- Adhering to Medication Schedule:
- Consistently take prescribed medications as directed, even when feeling well, to maintain asthma control and prevent flare-ups. Use devices such as inhalers or nebulizers correctly to ensure effective delivery of medication to the lungs.
- Monitoring Symptoms and Adjusting Treatment:
- Regularly monitor asthma symptoms and peak flow readings (if applicable) to track lung function. Communicate any changes or concerns to your healthcare provider promptly to adjust treatment as needed for optimal asthma management.
Step 2: Environmental Management
- Identifying Triggers:
- Asthma triggers vary among individuals and may include allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander), irritants (tobacco smoke, air pollution), respiratory infections, weather changes, and exercise.
- Reducing Exposure to Triggers:
- Take proactive measures to minimize exposure to identified triggers:
- Indoor Allergens: Use allergen-proof mattress and pillow covers, regularly vacuum carpets, and use air purifiers with HEPA filters.
- Outdoor Allergens: Monitor pollen counts and limit outdoor activities during peak pollen seasons. Shower and change clothes after outdoor activities to remove pollen.
- Irritants: Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke. Use masks or avoid areas with high air pollution levels.
- Take proactive measures to minimize exposure to identified triggers:
- Creating a Healthy Home Environment:
- Maintain good indoor air quality by ensuring proper ventilation, controlling humidity levels, and addressing mold or moisture issues promptly.
- Managing Workplace Exposures:
- Discuss potential asthma triggers in the workplace with your employer. Implement measures such as proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and workplace policies to reduce exposure to irritants or allergens.
Step 3: Lifestyle Adjustments
- Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle:
- Adopting overall healthy habits can support asthma management:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activities that promote cardiovascular health, such as swimming or walking, which can improve lung function and reduce asthma symptoms.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall health and immune function.
- Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight, as obesity can worsen asthma symptoms.
- Adopting overall healthy habits can support asthma management:
- Stress Management:
- Stress can trigger asthma symptoms. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, meditation, or hobbies that promote stress relief.
- Educational Support:
- Stay informed about asthma management through reliable sources, asthma education programs, and support groups. Knowledge empowers you to effectively manage your condition and advocate for your health needs.
Conclusion:
Achieving better asthma control involves a comprehensive approach that includes medication adherence, environmental management, and lifestyle adjustments. By working closely with healthcare providers, understanding asthma triggers, minimizing exposure to allergens and irritants, and adopting healthy habits, individuals can effectively manage asthma symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups. Remember, asthma management is a collaborative effort between you, your healthcare team, and your support network. With consistent effort and proactive steps, you can lead a fulfilling life while effectively managing asthma.