Introduction:
Fungal skin infections, caused by various types of fungi, are common conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. These infections can occur on different parts of the body and vary in severity from mild irritation to persistent and debilitating conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for fungal skin infections is essential for effective management and prevention. This blog provides a comprehensive overview of fungal skin infections, empowering readers with the knowledge to recognize, treat, and prevent these conditions effectively. Oxiconazole Nitrate Cream, which is used to treat fungal skin infections.
Types of Fungal Skin Infections:
- Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis):
- Athlete’s foot is a common fungal infection affecting the feet, particularly between the toes. It causes itching, redness, scaling, and sometimes blistering. The infection thrives in warm, moist environments like locker rooms and swimming pools. Zoderm E Cream works by causing holes in the fungal cell membranes and kills fungi.
- Ringworm (Tinea Corporis):
- Ringworm is a contagious fungal infection that can affect the skin on various parts of the body, including the scalp (tinea capitis), body (tinea corporis), and groin (tinea cruris or jock itch). It appears as a red, ring-shaped rash with raised edges and clear centers.
- Yeast Infections (Candidiasis):
- Candidiasis is caused by yeast-like fungi called Candida. It commonly affects moist areas of the skin such as the armpits, groin, and skin folds. Symptoms include redness, itching, and sometimes discharge in affected areas.
- Fungal Nail Infections (Onychomycosis):
- Fungal nail infections occur when fungi invade one or more of the nails. They typically cause thickening, discoloration (yellow or brown), and brittleness of the nails. Fungal nail infections can be challenging to treat and may require long-term therapy.
- Tinea Versicolor:
- Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection that affects the skin’s pigmentation, causing patches of lighter or darker skin. These patches may be more noticeable after sun exposure and typically appear on the chest, back, shoulders, and upper arms.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Fungal Growth Conditions:
- Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making areas such as sweaty socks and shoes, damp towels, and communal showers ideal breeding grounds for fungal infections.
- Weakened Immune System:
- Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Skin-to-Skin Contact:
- Direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces can transmit fungal infections.
- Poor Hygiene Practices:
- Not practicing good hygiene, such as sharing personal items like towels or razors, can increase the risk of fungal infections.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
- Common Symptoms:
- Itching (often intense)
- Redness and inflammation
- Scaling or flaking of the skin
- Rash with defined borders (ring-shaped in some cases)
- Discoloration of the affected skin or nails
- Diagnosis:
- Healthcare providers typically diagnose fungal skin infections based on clinical appearance and may confirm the diagnosis through:
- Visual examination of the affected area
- Skin scrapings for microscopic examination (KOH test)
- Culture of skin samples to identify the specific fungus
- Healthcare providers typically diagnose fungal skin infections based on clinical appearance and may confirm the diagnosis through:
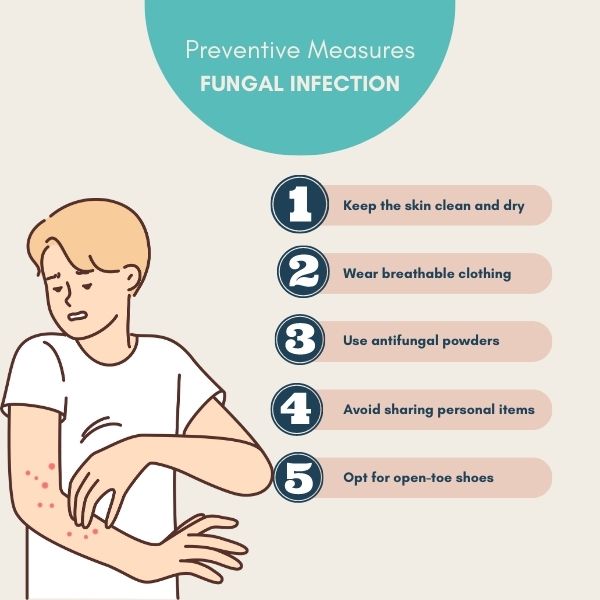
Prevention Strategies:
- Maintain Good Hygiene:
- Wash hands regularly, especially after touching infected areas or using communal facilities.
- Keep skin clean and dry, particularly in areas prone to sweating.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items:
- Do not share towels, socks, shoes, or other personal items that may harbor fungi.
- Wear Appropriate Clothing:
- Choose breathable fabrics and avoid tight-fitting clothing that traps moisture.
- Protective Measures in Public Spaces:
- Wear flip-flops or shower shoes in communal showers, locker rooms, and swimming pools.
- Treatment Options:
- Topical Antifungal Medications: Creams, ointments, or powders applied directly to the affected skin or nails.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: Prescribed for severe or persistent infections, especially fungal nail infections.
- Antifungal Shampoos: Used for fungal infections of the scalp (tinea capitis).
- Home Remedies and Adjunctive Treatments:
- Some people find relief with natural remedies such as tea tree oil or apple cider vinegar, although these should be used cautiously and in conjunction with medical advice.
- Follow-up and Monitoring:
- It is essential to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by healthcare providers to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
- Follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor progress and prevent recurrence.
Conclusion:
Fungal skin infections are common but manageable conditions that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. By understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options outlined in this blog, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and effectively manage fungal infections when they occur. Maintaining good hygiene practices, seeking prompt medical attention, and adhering to treatment plans are key to minimizing the impact of fungal skin infections and promoting skin health overall.
Remember, consulting with healthcare providers is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations tailored to your specific condition and needs. With knowledge and proactive measures, you can confidently navigate fungal skin infections and maintain healthy, resilient skin.